AN OVERVIEW OF CELL
● An `color{violet}"onion peel"` and/or `color{violet}"human cheek cells"` can be observed under the `color{violet}"microscope"`.
● The onion cell which is a `color{violet}"typical plant cell"`, has a distinct `color{brown}"cell wall"` as its outer boundary and just within it is the `color{brown}"cell membrane"`.
● The cells of the `color{violet}"human cheek"` have an outer membrane as the `color{violet}"delimiting structure"` of the cell.
● Inside each cell is a dense `color{violet}"membrane bound structure"` called `color{brown}"nucleus"`.
● This `color{violet}"nucleus"` contains the `color{brown}"chromosomes"` which in turn contain the genetic material, `color{brown}"DNA"`.
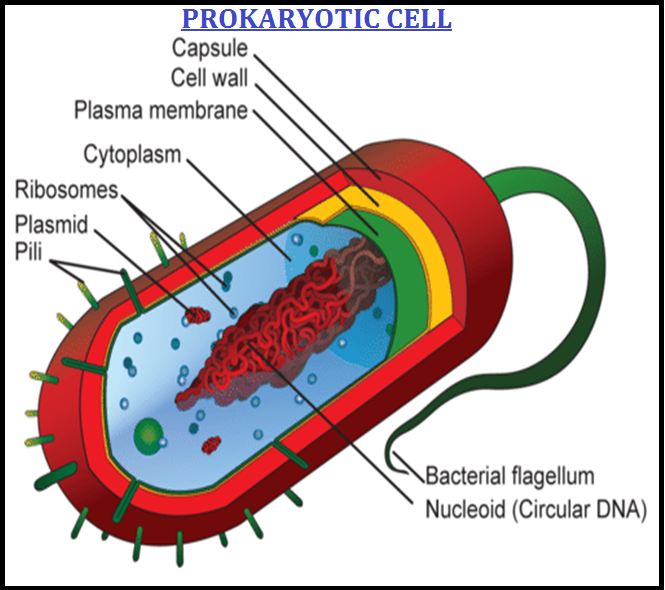
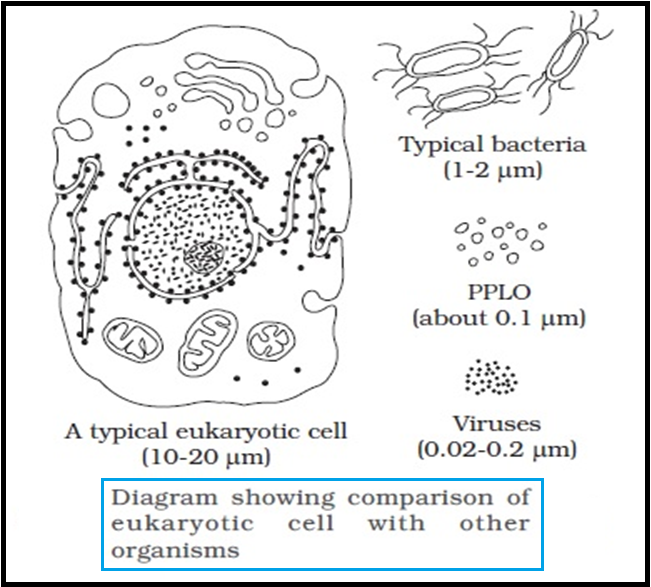
● Cells that have `color{violet}"membrane bound nuclei"` are called `color{brown}"eukaryotic"` whereas cells that `color{violet}"lack a membrane"` `color{violet}"bound nucleus"` are `color{brown}"prokaryotic"`.
● In both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, a `color{violet}"semi-fluid matrix"` called `color{brown}"cytoplasm"` occupies the volume of the cell.
● The cytoplasm is the `color{violet}"main arena of cellular activities"` in both the plant and animal cells.
● Various `color{violet}"chemical reactions"` occur in it to keep the cell in the `color{violet}"living state"`
● Besides the nucleus, the eukaryotic cells have other `color{violet}"membrane bound distinct structures"` called `color{brown}"organelles"` like the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), the golgi complex, lysosomes, mitochondria, microbodies and vacuoles.
● The prokaryotic cells lack such `color{violet}"membrane bound organelles"`.
● `color{brown}"Ribosomes"` are `color{violet}"non-membrane bound organelles"` found in all cells – both eukaryotic as well as prokaryotic.
● Within the cell, ribosomes are found not only in the cytoplasm but also within the `color{violet}"two organelles"` – `color{brown}"chloroplasts"` (in plants) and `color{brown}"mitochondria"` and on `color{brown}"rough ER"`.
● Animal cells contain another `color{violet}"non-membrane bound organelle"` called `color{brown}"centriole"` which helps in cell division.
● The onion cell which is a `color{violet}"typical plant cell"`, has a distinct `color{brown}"cell wall"` as its outer boundary and just within it is the `color{brown}"cell membrane"`.
● The cells of the `color{violet}"human cheek"` have an outer membrane as the `color{violet}"delimiting structure"` of the cell.
● Inside each cell is a dense `color{violet}"membrane bound structure"` called `color{brown}"nucleus"`.
● This `color{violet}"nucleus"` contains the `color{brown}"chromosomes"` which in turn contain the genetic material, `color{brown}"DNA"`.
● Cells that have `color{violet}"membrane bound nuclei"` are called `color{brown}"eukaryotic"` whereas cells that `color{violet}"lack a membrane"` `color{violet}"bound nucleus"` are `color{brown}"prokaryotic"`.
● In both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, a `color{violet}"semi-fluid matrix"` called `color{brown}"cytoplasm"` occupies the volume of the cell.
● The cytoplasm is the `color{violet}"main arena of cellular activities"` in both the plant and animal cells.
● Various `color{violet}"chemical reactions"` occur in it to keep the cell in the `color{violet}"living state"`
● Besides the nucleus, the eukaryotic cells have other `color{violet}"membrane bound distinct structures"` called `color{brown}"organelles"` like the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), the golgi complex, lysosomes, mitochondria, microbodies and vacuoles.
● The prokaryotic cells lack such `color{violet}"membrane bound organelles"`.
● `color{brown}"Ribosomes"` are `color{violet}"non-membrane bound organelles"` found in all cells – both eukaryotic as well as prokaryotic.
● Within the cell, ribosomes are found not only in the cytoplasm but also within the `color{violet}"two organelles"` – `color{brown}"chloroplasts"` (in plants) and `color{brown}"mitochondria"` and on `color{brown}"rough ER"`.
● Animal cells contain another `color{violet}"non-membrane bound organelle"` called `color{brown}"centriole"` which helps in cell division.